
Research Projects
 |
Research Projects |
page under construction...
Main topics: Computer Vision and Machine Learning.
Recent projects: Video understanding (text & images), Image
segmentation and recognition, approximate inference for Graph Matching
and MRFs
| Video and Text Alignment
Related publications: Timothee Cour, Chris Jordan, Eleni Miltsakaki, Ben Taskar. Movie/Script: Alignment and Parsing of Video and Text Transcription. Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2008.[videos: retrieval of actions and character naming] |
| Approximate inference
Related publications: Timothee Cour, Jianbo Shi. Solving Markov Random Fields with Spectral Relaxation. Eleventh International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), 2007.Timothee Cour, Praveen Srinivasan, Jianbo Shi. Balanced Graph Matching. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2006 |
| Object specific segmentation and pose estimation
Related publications: Timothee Cour, Jianbo Shi. Recognizing objects by piecing together the Segmentation Puzzle. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2007. |
|
Multiscale segmentation
We present a multiscale graph-based image segmentation algorithm. In contrast to most multiscale image processing, this algorithm works on multiple scales of the image in parallel, without iteration, to capture both coarse and fine level details. We demonstrate that large image segmentation graphs can be compressed into multiple scales capturing image structure at increasingly large neighborhood. The algorithm has O(N) time complexity, allowing to segment large images with typically N = 1000 x 1000 pixels. Related publication:
Spectral
Segmentation with Multiscale Graph Decomposition.
Timothee
Cour, Florence Benezit, Jianbo Shi.
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2005. [pdf][abstract] |
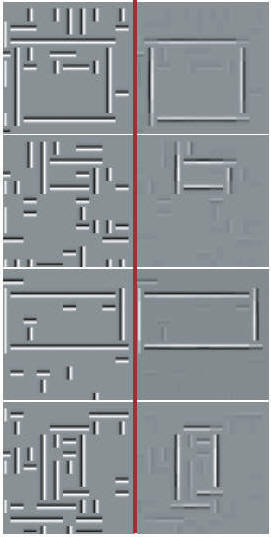 |
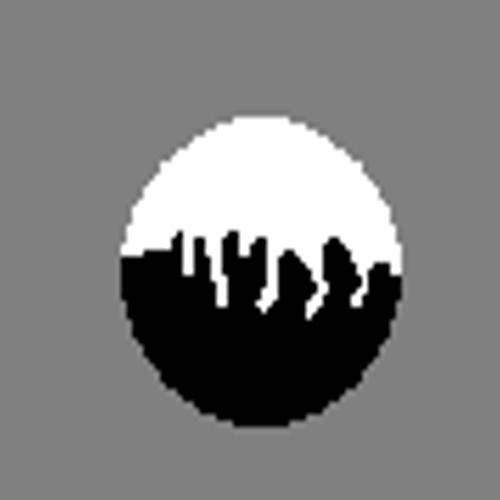
Learning image
segmentation and recognition We present a general graph learning algorithm for spectral graph partitioning, that allows direct supervised learning of graph structures. Learning is based on gradient descent in the space of graph weights, using derivatives of eigenvectors. This algorithm effectively learns a graph capable of memorizing and retrieving multiple patterns given noisy inputs. We experimented on segmentation and recognition tasks, including bottom-up geometric shape extraction with top-down priors, and hand-written digit recognition. Related publications:
|
 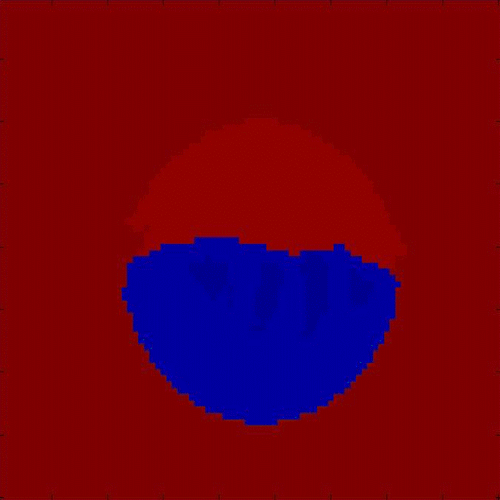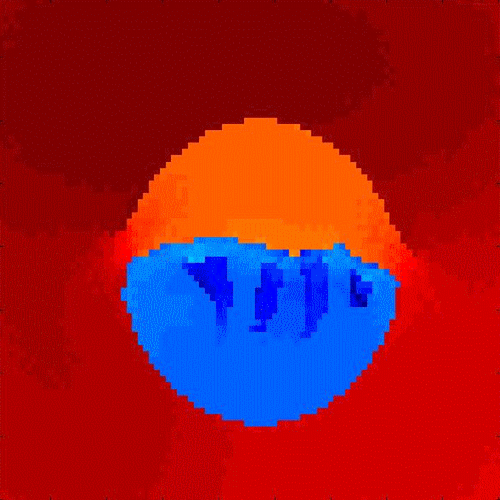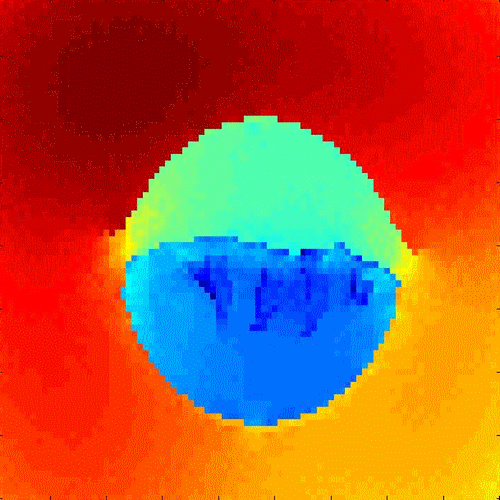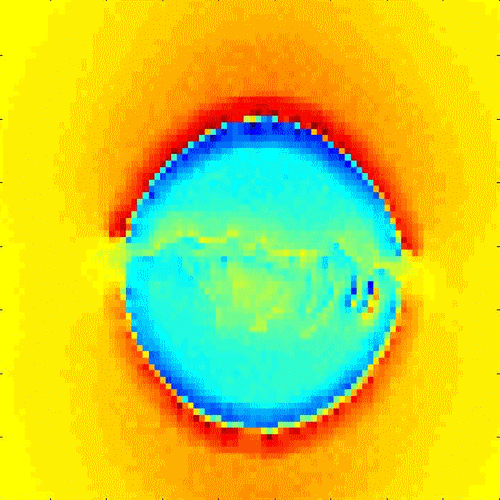 |
Shape-based object
segmentation
internship at University of Pennsylvania, GRASP
Laboratory, (2003) Designed an algorithm to segment objects using shape cues and pixel cues, combined into a consistent grouping of contour and region.
|
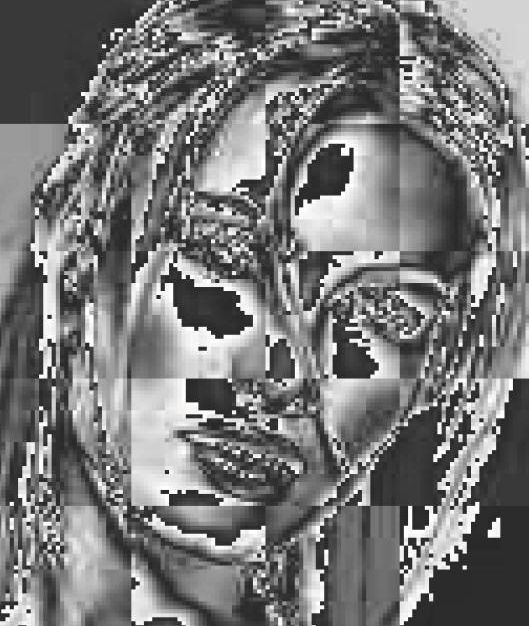 |
Image Compression and
Super-Resolution using Wavelets
[pdf]
Ecole Polytechnique,
Department of Applied Mathematics (2002) Developed an original learning algorithm of super-resolution to optimize the wavelet compression. Increased compression rate over classical linear predictions.
|
|
|
A chess engine and chess-playing autonomous robot
[pdf]
Ecole Polytechnique,
Department of Computer Science (2002) Digital camera, robot and chess engine controlled by a gui. Actual games played by the robot against a human opponent. Robust recognition of chess position under various conditions of light and board position. Used an alpha-beta pruning algorithm with various heuristics |
 |
A
biologically-inspired neural network for handwritten character
recognition [pdf] [slides]
Ecole Polytechnique,
Department of Computer Science (2001) |